The data center is the heart of a fiber optic network. To ensure its long-term reliable network performance, all the optical equipment within data center should be well organized. However, the current multi-fiber counts and high-density optical cabling put strain in the cable management. Fiber patch enclosure provides solid fiber-optic-link protection and space-saving cable management, which is becoming a must-have component in data center. There are several fiber optic enclosures available on the market that are widely utilized in data center or server room. This article will briefly introduce the commonly used fiber enclosure designs to better meet your data center requirement. LC to LC fiber cable and patch panels are mounted in a fiber enclosure in the following picture.

Fiber Enclosure Designs
Rack mount fiber enclosure is the commonly used type in data center as it provide a convenient and rugged termination point for fiber jumper cables. This rack mount enclosures offer a flexible connectivity system using a variety of adapter plates and MPO cassettes. The enclosures work equally as well with armored cable as they do with multiple trunk cables and are available in 1U-4U versions.
1U enclosures fit standard 19-inch racks and have rear cable management rings. 2U, 3U and 4U enclosures are designed for side or rear trunk cable entry, have removable front and rear covers, edge guards on the front for cable assembly protection and front and rear cable management rings. 2U, 3U and 4U enclosures also fit standard 19 and 23-inch racks and have a clear plastic, removable front door that can be outfitted with a label for easy identification of connections.
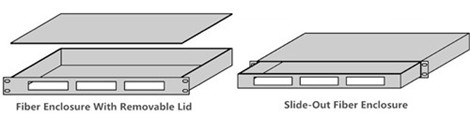
Except for different size, there are two types of rack mount enclosures: fiber enclosure with a removable lid and slide-out fiber enclosure (see in the following figure). The slide-out version is typically more expensive than the other version. But slide-out fiber enclosure can allow customers to remove the whole enclosure from the rack, thus, it can provide easier internal fiber connection access.
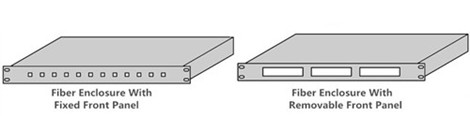
As for the design of the fiber enclosure front panel, two commonly used types are fixed front panels and removable front panel. The fixed front panel can be loaded with appropriate fiber optic adapters, while the removable front pane can accommodate several fiber optic adapter panels or cassettes just as seen in the following image.
How to Select the Fiber Enclosure
If this is your first time to install a fiber optic network, you should follow the instructions below. Only in this way can you satisfy your installation requirement, and matched your budget as well.
- Physical requirement
First, list all the requirement that will be mounted in the enclosure and their complete measurements:height, depth, width, weight. All of these figures will ultimately determine what type of fiber enclosure you will need. Note that always select a bigger fiber enclosure for all your existing equipment as well as for future proof.
- Critical accessories
A fiber enclosure should provide plenty of grommeted access points through the rear and top of the cabinet, as well as through the bottom for raised floor installations. Not only are the fiber optic cables mounted in the fiber enclosure, but devices like hubs, routers, patch panels, and monitors are needed to be mounted in the enclosure-network.
All servers should be protected by an uninterruptible power supply(UPS) system, available in a variety of rack-mount configurations. Thus power protection is needed. Remember that any accessories that are not rack-mountable will require additional trays, shelves and mounting accessories.
- Budget
Money is always a main considerations. Thus choose the fiber enclosure that can meet your premium features at a very competitive price is the number one task. People are usually in a dilemma about whether to choose a equipment that are suitable for now or the expensive one for future proof. It is hard to say, but a premium enclosure is a durable item that will provide services for years to come.
Summary
High density fiber enclosures can maximize the amount of active equipment in a data center by minimizing the footprint of the networking infrastructure, but there’s a problem—all that fiber in a small amount of space creates problems when changes need to be made. Therefore for easiest access, quick-release side panels should be a top priority when selecting an enclosure.
With several years of experience in fiber optic cabling solutions, FS.COM offers the world-class optical products and services to maximize the performance and scalability of your data center applications. Our fiber enclosures provide the highest fiber densities and port counts in the industry contributing to maximizing rack space utilization and minimizing floor space. For more detailed information, you can directly contact us.