Small form-factor pluggable (SFP) is a prevailing type of optical transceivers in the market widely utilized for Gigabit Ethernet application. As it has the same function with GBIC but with a smaller size, SFP transceiver is also called mini-GBIC. Optical transceivers are typically designed to both transmit and receive electrical optical signals under the Multi-Source Agreement. Each SFP module can support data rates from 1Gbps to 10Gbps. And there are a number of SFP modules and network accessories available for you to select from. Which one suits you better? The following article will dig deeper into the SFP transceivers that will help decide which one will work best for you.
SFP transceivers have a variety of different transmission and receiving type, users can select the appropriate transceiver for each link, to provide the optical performance can be achieved based on the available fiber type (such as a multimode fiber or single-mode fiber). Optical SFP modules available are generally divided into the following categories. Figure 1 displays the basic components of a SFP transceiver.
1000BASE-LX—Specified in IEEE 802.3 Clause 38, 1000BASE-LX uses a long wavelength laser (1270-1355 nm), and a maximum RMS spectral width of 4nm. 1000BASE-LX is designed to cover a distance of up to 10 km over 10µm single-mode fiber. 1000BASE-LX can also run over all common types of multimode fiber with a maximum segment length of 550 m. For link distances greater than 300 m, the use of a special launch conditioning patch cord may be required. E1MG-LX-OM is Brocade 1000BASE-LX SFP that can work over a distance of 10km.
1000BASE-EX—1000BASE-EX is not a standard but industry accepted term for Gigabit Ethernet transmission. It is very similar to 1000BASE-LX10 but achieves longer distances up to 40 km over a pair of single-mode fibers due to higher quality optics than a LX10, running on 1310nm wavelength lasers. It is sometimes referred to as LH (Long Haul).
1000BASE-ZX—1000BASE-ZX is also a non-standard but multi-vendor term using 1,550nm wavelength to achieve distances of at least 70 kilometers over single-mode fiber. Some vendors can specify distances up to 120 kilometers over single-mode fiber. Ranges beyond 80 km are highly dependent upon the path loss of the fiber in use, specifically the attenuation figure in dB per km, the number and quality of connectors/patch panels and splices located between transceivers.
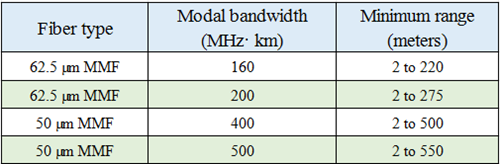
1000BASE-SX—1000BASE-SX is a Gigabit Ethernet standard for operation over multimode fiber using a 770 to 860 nm, near infrared (NIR) light wavelength for a maximum of 550m at 1.25 Gbit/s (gigabit Ethernet) or 150m at 4.25 Gbit/s (Fibre Channel). Take EX-SFP-1GE-SX as an example, it is 1000BASE-SX SFP that can support a link length of 550m over OM2 cable. Figure 2 shows that EX-SFP-1GE-SX inserts into a Juniper SRX210.
1000BASE-BX10—1000BASE-BX10 is capable of up to 10 km over a single strand of single-mode fiber, with a different wavelength going in each direction. The terminals on each side of the fiber are not equal, as the one transmitting downstream uses the 1490nm wavelength, and the one transmitting upstream uses the 1310nm wavelength.
1000BASE-T—It is a standard for Gigabit Ethernet copper cabling. The maximum length of 1000GBASE-T is 100 meters. 1000BASE-T must use Category 5 cable or better (including Cat 5e and Cat 6. 1000BASE-T can be used in data centers for server switching, for uplinks from desktop computer switches, or directly to the desktop for broadband applications.
1000BASE-TX—Created by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), 1000BASE-TX (TIA/EIA-854) is a standard similar to 1000BASE-T that was simpler to implement. Compared with 1000BASE-T, this simplified design would have reduced the cost of the required electronics by only using two unidirectional pairs in each direction instead of 4 bidirectional. However, this solution has not been widely used largely due to the required Category 6 cabling and the rapidly falling cost of 1000BASE-T products.
Recommended Information
It is known that there is no visual difference between the bare SFP modules, so how to differ them? Smart manufacturers figure a way out by marking the color of pull ring to distinguish generally. For example: black pull ring is multimode, the wavelength is 850 nm; blue is the 1310nm module; yellow is the 1550nm module; purple is the 1490nm module and so on. If you are confused with the specifications of the SFP modules, you should find a reliable vendor to help you. Fiberstore provides a variety of SFP modules including 100BASE SFP, 1000BASE SFP, BiDi SFP, CWDM/DWDM SFP, SONET/SDH SFP and 2G/4G FC SFP. Our SFP modules are fully compatible with major brand. For more information about SFP transceivers, please feel free to contact us.