As audio video systems and installations have become more complex over time, it is common for people to use HD TVs, HD media players, and other home theater systems. Additionally there seemed to be a big variance in quality between brands, especially when it came to extending HDMI signals. Therefore, the introduction of HDMI technology is a game changer and highly appreciated by overall users in this days. Just as fiber jumper connecting optical equipment, HDMI cables offer long-distance HD audio and video signals transmission playing an important role in achieving brilliant performance. Today’s article will have a brief introduction to this cable.
HDMI Cable
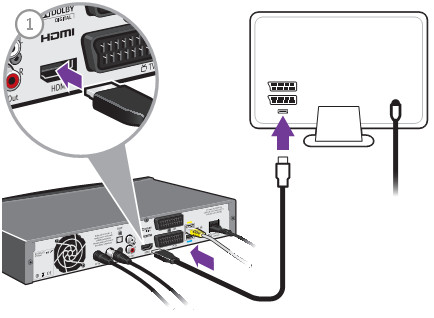
HDMI ((High-Definition Multimedia Interface) cable is composed of four shielded twisted pairs with several separate conductors for transferring data over video/audio devices. A HDMI cables are defined into two cable categories: one is the Category 1-certified cables, known as standard HDMI cables, the other is Category 2-certified cables, also called high speed HDMI cables. HDMI cables has not been specified the transmission length. A cable of about 5 meters (16 feet) can be manufactured to Category 1 specifications easily and inexpensively by using 28 AWG conductors. With better quality construction and materials, including 24 AWG conductors, an HDMI cable can reach lengths of up to 15 meters (49 feet). HDMI cables are expensive than the regular Cat6/Cat7 cables. Just as anything else, whether you want to use the expensive but high-performance HDMI cables or cheap but low-performance Category copper cables like Cat5e/Cat6, it depends on what inputs you tech has. The below part lists the current usage of HDMI cables, and you can look at the solutions that interest you. The following image shows the image of a HDMI cables connecting box and HDMI socket of TV.
Difference Between an HDMI Cable and a DVI Cable
HDMI cable and DVI cable as two two input-output media interfaces in home network are posing difficulty in distinguishing them. In fact, the biggest difference between these two transmission media lies in their layout. An HDMI cable is more compact and resembles a USB cable, while a DVI cable is usually bigger in size. Another major difference is in capability: the HDMI supports audio and video, whereas the DVI is strictly video-only.
Applications of HDMI Cables
- Boosted HDMI: HDMI cables, with a booster integrated into their structure use the 5v power rail of the HDMI signal to carry the data further without loss of fidelity. This cable, compared with the normal HDMI cable, is intended to make longer cable runs, but it can also be used to make a short cable thinner and much more flexible. HDMI cables with integrated booster chipsets are more expensive than their basic counterparts, and so far only cater to 1080p content due to the loss of bandwidth over the extended length, but they can reach 40 meters.
- HDMI over CAT: It is not a new concept to use Cat5 or Cat6 cables to extend an AV source. HDMI recently make use of this technology for stable extended runs—sometimes even using existing network cabling. Due to bandwidth limitations, most CAT extenders only support 1080p, but some can handle 3D, too. Configuration is more complex than regular cables, and interference can be a big problem in some environments, but with a good HDMI over Cat5/6 Extender, you can run 50 meters.
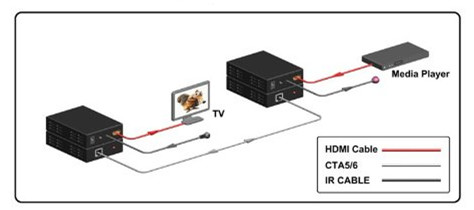
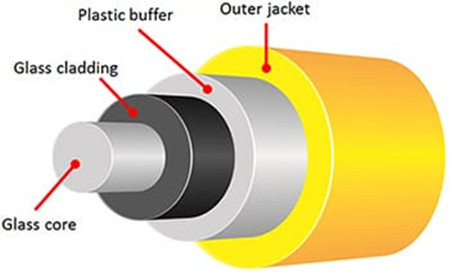
- HDMI over Fiber Optics: Fiber optics for HDMI, compared with HDMI over CAT, carries the highest price premium, but they have the much better capacity to outstrip copper based cables for distance by a large margin. The added benefit to this cable type is flexibility with a maximum distance of 45 meters. The optical core is much smaller than Boosted HDMI, but can go the same distances. Note that some companies have kits which run much longer, but it of course will cost far more!
- HDMI over Wireless: Wireless technologies vary between models, but one thing they have in common is they don't generally go as far as cables do. Line of sight is 10 to 15 meters, and through walls can be as low as 5 to 8 meters. Unless you can't run a cable at all, a lead will beat Wireless every time. Wireless is also limited by bandwidth to 1080p, and only the best units can handle 3D.
Some Terms Appeared in the Above Part
1080p refers to an HDTV format which has 1080 horizontal lines of resolution. The p stands for progressive scan. The traditional analog video uses an interlaced scan, which draws the odd lines, then even lines of each frame in sequence.
AWG is short for American Wire Gauge, which is a common unit of wire measurement. AWG expressed in a HDMI cable refers to the size of the conductors within the cable. With wire gauges, smaller numbers actually refer to larger wires. This means a 24 AWG cable has a thicker conductor than a 28 AWG cable. The benefit of a thicker conductor is the ability to effectively transmit an HD signal.
Plenum refers to the air-handling spaces in building construction above the ceiling and beneath the floors. Some building codes require Plenum-rated cable, which has a low-smoke jacket that burns slower in the event of a fire and emits less toxic smoke.
Summary
This article isn’t a definitive guide to HDMI cables, but for the sake of simplicity we just provide some basic information about industrial and commercial applications of HDMI cables. If you are on the fence to install a fiber optic network, always use the shortest length of cable you can live with, and ensure they're certified by the industry bodies. What’s more, it is advisable for you to save your money for other home network components and get your HDMI cables as cheaply as possible. FS.COM offers a full range of optical products including fiber optic cables (e.g. SC to LC patch cable), copper cables (like Cat5e, Cat6), optical transceivers and so on. If you want to know more information about our products, please send your request to us.