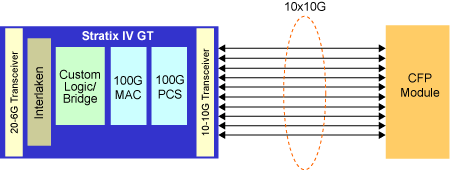
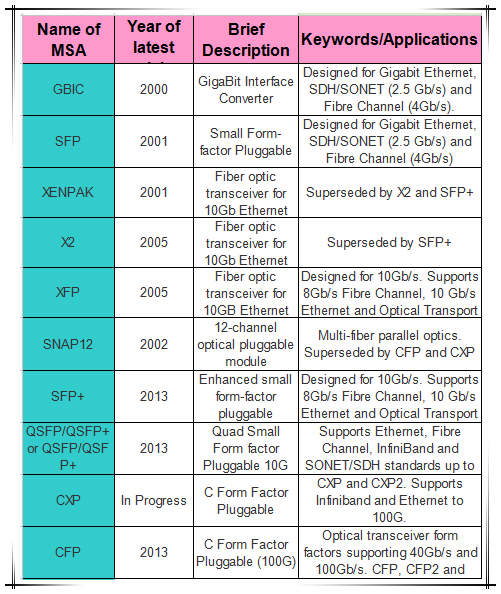
During the past few years, 40G technology has dominated telecommunications. But now, with the introduction of the 100G technology, everyone is talking about 100 Gbps as the next generation. Whether willing or not, IT managers and data center designers have to consider migrate their network to 100 Gbps in the near future. And CFP is designed to fulfil the deployment of 100G network for companies and enterprises.
Brief Introduction to 100G CFP Optics
CFP transceiver was designed after SFP transceiver interface, but it supports much larger internet speed, which is realized by using 10×10Gbit/s in each direction (RX, TX). Here the C stands for 100 in Roman numerals (centum). We can infer from the name that CFP is introduced to serve as optical transceiver for 100G interfaces. Since the electrical connection of the CFP uses 10×10Gbit/s lanes in every direction, the optical connection can support both 10×10Gbit/s and 4×25Gbit/s variants of 100Gbit/s interconnects (typically known as 100GBASE-LR10 and 100GBASE-LR4 in 10km SMF reach, and 100GBASE-ER10 and 100GBASE-ER4 in 40km SMF reach, and 100GBASE-SR10 in 100 meter MMF reach respectively.)
CFP transceiver was designed after SFP transceiver interface, but it supports much larger internet speed, which is realized by using 10×10Gbit/s in each direction (RX, TX). Here the C stands for 100 in Roman numerals (centum). We can infer from the name that CFP is introduced to serve as optical transceiver for 100G interfaces. Since the electrical connection of the CFP uses 10×10Gbit/s lanes in every direction, the optical connection can support both 10×10Gbit/s and 4×25Gbit/s variants of 100Gbit/s interconnects (typically known as 100GBASE-LR10 and 100GBASE-LR4 in 10km SMF reach, and 100GBASE-ER10 and 100GBASE-ER4 in 40km SMF reach, and 100GBASE-SR10 in 100 meter MMF reach respectively.)
Different Types of 100G CFP
There are several CFP types to be introduced—CFP, CFP2 and CFP4. CFP2 and CFP4 are the upgraded generation of CFP. Among them, the size of CFP is the largest. CFP2 is half the size of CFP while CFP4 is the half size of CFP2. And the features of the three different types have been summarized in the following texts. One thing that needs to be noted is that although they are not interchangeable, but could be interoperable at the optical interface with appropriate connectors.
There are several CFP types to be introduced—CFP, CFP2 and CFP4. CFP2 and CFP4 are the upgraded generation of CFP. Among them, the size of CFP is the largest. CFP2 is half the size of CFP while CFP4 is the half size of CFP2. And the features of the three different types have been summarized in the following texts. One thing that needs to be noted is that although they are not interchangeable, but could be interoperable at the optical interface with appropriate connectors.

Features and Benefits of CFP:
- Supports 40G and 100G Ethernet CFP optical transceivers
- Capable of side by side mounting as well as “belly to belly” mounting
- Provides full EMI shielding
- Uses a universal rail for both left and right positions
- Allows integration of host PCB to host bezel (face plate) by either of two methods for manufacturing flexibility.
Features and Benefits of CFP2 and CFP4:
- Up to 28 Gbps per lane – 2.8 times faster than current CFP products
- High density, 0.6mm contact pitch
- Provides one of the industry’s leading Signal Integrity (SI) performance for 28 Gbps per lane
- Features a ruggedized cage construction for a more robust solution to help mitigate cage warping
- Flexible design options to address your needs including ganged cages, heat sinks, single-sided and belly-to-belly mounting styles, light-pipes, and the capability to support mid- to long-reach applications
FS 100G CFP Solution
As one of the leading providers in optical communication , FS provides customers with transceivers that are manufactured at the highest quality of standards in the industry. All the CFP transceivers mentioned above, including both CFP2 and CFP4, are available in our website. And every transceiver is individually tested on corresponding equipment such as Cisco, Arista, Juniper, Dell, Brocade and other brands, and passed the monitoring of our intelligent quality control system. Also, all the products in FS are fully warranted against defects in material and workmanship with a lifetime guarantee.
As one of the leading providers in optical communication , FS provides customers with transceivers that are manufactured at the highest quality of standards in the industry. All the CFP transceivers mentioned above, including both CFP2 and CFP4, are available in our website. And every transceiver is individually tested on corresponding equipment such as Cisco, Arista, Juniper, Dell, Brocade and other brands, and passed the monitoring of our intelligent quality control system. Also, all the products in FS are fully warranted against defects in material and workmanship with a lifetime guarantee.
Conclusion
2017 has witnessed the prosperity of the telecommunication market. Many research company predicts that the market of 2018 for telecommunication field will continue to thrive. With such a bright future, fiber optics market attracts a wide attention and many vendors want a piece of the pie. At present, 40G is ubiquitous in the data center and 100G is accelerating. As for the optical transceiver, it has been developed in the past decades to adapt to the high-speed requirement from 1G to 40G even to 100G. Believe it or not, 100G is on the way. Don’t wait to get fully prepared for the upcoming 100G era with CFP transceivers.
2017 has witnessed the prosperity of the telecommunication market. Many research company predicts that the market of 2018 for telecommunication field will continue to thrive. With such a bright future, fiber optics market attracts a wide attention and many vendors want a piece of the pie. At present, 40G is ubiquitous in the data center and 100G is accelerating. As for the optical transceiver, it has been developed in the past decades to adapt to the high-speed requirement from 1G to 40G even to 100G. Believe it or not, 100G is on the way. Don’t wait to get fully prepared for the upcoming 100G era with CFP transceivers.