Transceiver modules can be classified into different categories based on several different criteria. Package, transmission distance, wavelength, work rate, fiber mode, and connector type are all the common characteristics used for defining fiber optic transceivers. The following is a brief introduction to some of the characteristics used in classifying transceiver modules.
Package of Fiber Optic Transceiver
According to the optical module package, fiber optic transceivers can be divided into SFP, SFP+, XFP, GBIC, X2, XENPAK, QSFP+, PON, CSFP, CFP, 1X9 and SFF. Each package has its unique feature. Nowadays, SFP, SFP+, XFP and QSFP+ are the popular packages and they have been widely used in many fields, such as video communication field, aerospace, fiber to the home and so on. The image below shows a compatible HP SFP transceiver module.
According to the optical module package, fiber optic transceivers can be divided into SFP, SFP+, XFP, GBIC, X2, XENPAK, QSFP+, PON, CSFP, CFP, 1X9 and SFF. Each package has its unique feature. Nowadays, SFP, SFP+, XFP and QSFP+ are the popular packages and they have been widely used in many fields, such as video communication field, aerospace, fiber to the home and so on. The image below shows a compatible HP SFP transceiver module.
Data Transfer Distance
In relation to data transfer distance, one major difference is multi-mode versus single-mode transceivers. For instance, a multi-mode transceiver will typically cover a distance of 100 m to 500 m. A single-mode transceiver can transmit a distance from 2 km to 120 km. This is an important aspect that people should consider when selecting a transceiver for an application. If the transmission distance is not adequate, the application will not work properly. Data transmission distance may be affected by whether the transceivers are single fiber or dual fiber.
In relation to data transfer distance, one major difference is multi-mode versus single-mode transceivers. For instance, a multi-mode transceiver will typically cover a distance of 100 m to 500 m. A single-mode transceiver can transmit a distance from 2 km to 120 km. This is an important aspect that people should consider when selecting a transceiver for an application. If the transmission distance is not adequate, the application will not work properly. Data transmission distance may be affected by whether the transceivers are single fiber or dual fiber.
Wavelength
Wavelength is the distance between repeating units of a propagating wave of a given frequency. Fiber optics transceivers transmit signal typically around 850, 1300 and 1550 nm. Multi-mode fiber is designed to operate at 850 and 1300 nm, while single-mode fiber is optimized for 1310 and 1550 nm.
Wavelength is the distance between repeating units of a propagating wave of a given frequency. Fiber optics transceivers transmit signal typically around 850, 1300 and 1550 nm. Multi-mode fiber is designed to operate at 850 and 1300 nm, while single-mode fiber is optimized for 1310 and 1550 nm.
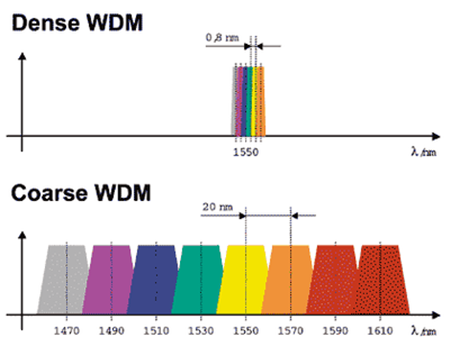
Recent telecom systems use wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM), either DWDM (dense WDM) or CWDM (coarse WDM). For the fiber optic transceiver modules, the common wavelength (see in below image) includes 850 nm, 1279 nm, 1310 nm, 1330 nm, 1490 nm, 1510 nm, 1550 nm and 1610 nm. In the CWDM system, the wavelength range is from 1270 nm to 1610 nm, 20nm as a wave band. In the DWDM system, the wavelength range is also from 1270 nm to 1610 nm, but 0.8nm as a wave band.
Work Rate
The above type of classification brings two distinct types—full duplex mode and half duplex mode. The full duplex mode occurs when the data transmission is transmitted by two different transmission lines. There is communication at both ends of the device and is used for both sending and receiving operations. In this type of transceiver configuration, there is typically, no time delay generated by the operation.
The above type of classification brings two distinct types—full duplex mode and half duplex mode. The full duplex mode occurs when the data transmission is transmitted by two different transmission lines. There is communication at both ends of the device and is used for both sending and receiving operations. In this type of transceiver configuration, there is typically, no time delay generated by the operation.
The half-duplex mode is used with a single transmission line that is used for both reception and transmission. The communication cannot occur simultaneously in the same direction. That’s why it’s called the half-duplex system.
Managed Versus Unmanaged Transceivers
Unmanaged Ethernet optical transceivers are typically plug and play. They may have electrical interfaces with hardware DIP switch settings mode. With managed Ethernet fiber optic transceivers, they support a carrier-grade network management.
Unmanaged Ethernet optical transceivers are typically plug and play. They may have electrical interfaces with hardware DIP switch settings mode. With managed Ethernet fiber optic transceivers, they support a carrier-grade network management.
Conclusion
When you design for fiber optic transceiver, these classification criteria will come in handy. Fiberstore, as an professional telecommunication manufacturer, provides a large amount of fiber optic transceiver modules like SFP+ transceiver, X2 transceiver, XENPAK transceiver, XFP transceiver, SFP transceiver, GBIC transceiver, CWDM/DWDM transceiver, etc. J4858C, DS-SFP-FC8G-SW, DEM-310GT and Finisar FTLX1471D3BCL are all available at Fiberstore. They are fully compatible with major brand. If you have any question, please contact us directly.
When you design for fiber optic transceiver, these classification criteria will come in handy. Fiberstore, as an professional telecommunication manufacturer, provides a large amount of fiber optic transceiver modules like SFP+ transceiver, X2 transceiver, XENPAK transceiver, XFP transceiver, SFP transceiver, GBIC transceiver, CWDM/DWDM transceiver, etc. J4858C, DS-SFP-FC8G-SW, DEM-310GT and Finisar FTLX1471D3BCL are all available at Fiberstore. They are fully compatible with major brand. If you have any question, please contact us directly.


